Fuel tanks play a crucial role in various sectors, including automotive, industrial, aviation, and marine. Whether it’s powering vehicles or facilitating operations in industrial plants, the efficient functioning of fuel tanks is essential for safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. However, without proper maintenance, fuel tanks can pose significant risks, leading to accidents, operational disruptions, and financial losses. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of fuel tank maintenance, common issues that arise when maintenance is neglected, and best practices to ensure the longevity and efficiency of fuel tanks.
Importance of Fuel Tank Maintenance
Safety Considerations
Regular maintenance of fuel tanks is paramount for ensuring safety in any application. Neglected fuel tanks can develop leaks, leading to fuel spills that pose fire hazards and environmental risks. In industries where flammable or hazardous materials are stored, such as petroleum refineries or chemical plants, the consequences of a fuel tank failure can be catastrophic. Proper maintenance helps identify and address potential safety risks before they escalate into emergencies.
Operational Efficiency
Well-maintained fuel tanks contribute to operational efficiency by ensuring a consistent supply of fuel for machinery and vehicles. Any downtime caused by fuel tank issues can disrupt production schedules, leading to delays and financial losses. Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, optimizing productivity and minimizing disruptions in various industries.
Cost Savings
Investing in fuel tank maintenance can result in significant cost savings in the long run. By detecting and addressing issues early on, maintenance helps prevent costly repairs or replacements down the line. Moreover, efficient fuel storage and management practices can reduce fuel wastage and improve fuel efficiency, leading to lower operational costs over time.

Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements regarding the maintenance of fuel tanks. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also essential for mitigating risks and ensuring environmental protection. Regular maintenance helps organizations adhere to relevant standards and regulations, avoiding potential fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Common Issues in Fuel Tanks
Contamination
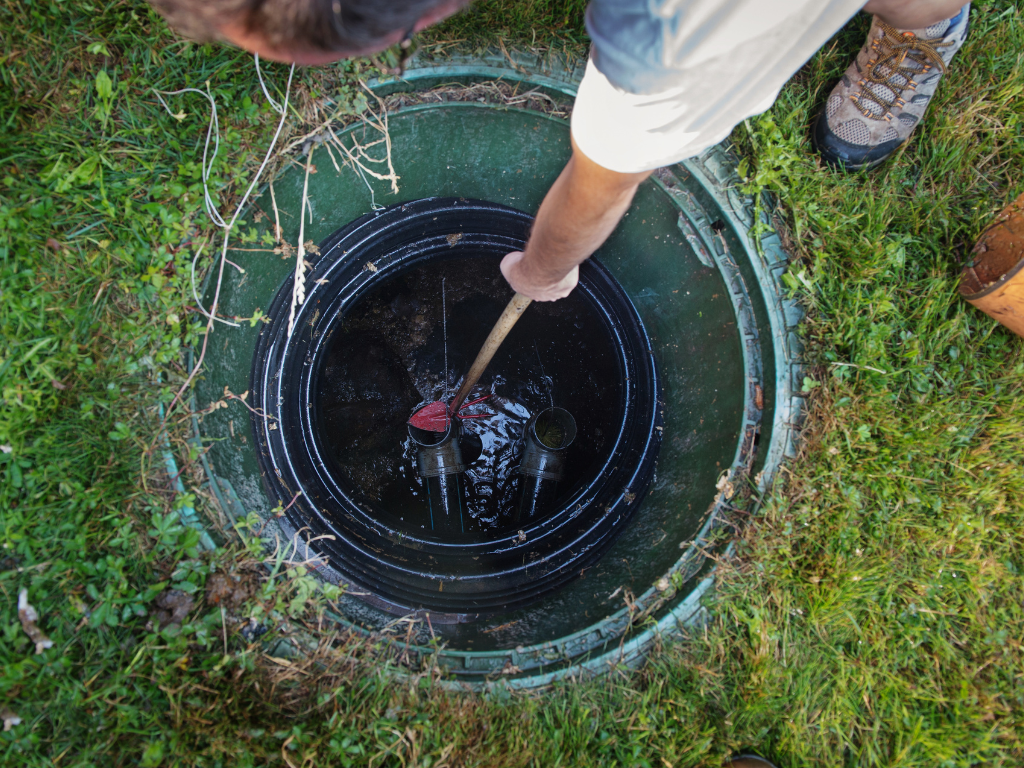
Contamination is a prevalent issue in fuel tanks and can occur due to various factors, including water ingress, microbial growth, and the accumulation of debris. Water, in particular, can promote corrosion and microbial contamination, compromising fuel quality and leading to engine problems. Regular inspection and cleaning are essential for preventing contamination and preserving fuel integrity.
Corrosion
Corrosion is another significant concern for fuel tanks, especially those made of metal such as steel or aluminum. Internal corrosion can occur due to the presence of water or corrosive substances in the fuel, while external corrosion may result from exposure to environmental elements. Corrosion weakens the structural integrity of fuel tanks and increases the risk of leaks. Protective coatings, cathodic protection systems, and regular inspections are effective measures for mitigating corrosion risks.
Structural Integrity
Over time, fuel tanks may develop cracks, leaks, or other structural issues that compromise their integrity. These issues can result from factors such as aging, mechanical stress, or environmental conditions. Regular inspection and timely repairs are crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of fuel tanks and preventing catastrophic failures.
Fuel Degradation
Fuel degradation refers to the deterioration of fuel quality over time, leading to reduced performance and efficiency. Factors such as oxidation, contamination, and microbial activity can contribute to fuel degradation, resulting in engine problems and increased emissions. Proper fuel storage practices, including the use of additives and regular fuel testing, help mitigate the effects of fuel degradation and ensure optimal engine performance.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular Inspection
Routine inspection is the cornerstone of fuel tank maintenance. Visual inspections should be conducted regularly to identify any signs of damage, corrosion, or contamination. Additionally, advanced inspection techniques such as ultrasound testing or pressure testing can provide insights into the condition of the fuel tank’s internal components.
Cleaning and Decontamination
Cleaning and decontamination are essential maintenance procedures to remove accumulated debris, water, and microbial growth from fuel tanks. Depending on the type of contamination, various cleaning methods such as mechanical cleaning, chemical treatments, or biological control agents may be employed. AquaQuick, a leading provider of fuel tank cleaning solutions, offers innovative products designed to effectively remove contaminants and restore fuel tank integrity.
Corrosion Prevention
Preventing corrosion is critical for extending the lifespan of fuel tanks and ensuring their reliable performance. Protective coatings, such as epoxy or polyurethane coatings, create a barrier between the tank’s metal surface and corrosive substances in the fuel. Cathodic protection systems, including sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems, help inhibit corrosion by directing electrical currents away from the tank’s metal components.
Structural Repairs
Timely repair of any damage or defects in fuel tanks is essential for maintaining their structural integrity. Welding, patching, or lining may be used to repair leaks or cracks in the tank’s walls. It’s crucial to address structural issues promptly to prevent further damage and minimize the risk of fuel leaks or spills.
Fuel Quality Management
Managing fuel quality is integral to fuel tank maintenance, as poor-quality fuel can lead to engine problems and equipment failures. Regular fuel sampling and testing help monitor fuel quality parameters such as moisture content, sediment levels, and octane rating. Additionally, the use of fuel additives, such as stabilizers or biocides, can help preserve fuel integrity and prevent degradation.
Best Practices for Different Types of Fuel Tanks
Fuel tanks come in various types and serve different purposes across industries. Implementing best practices tailored to specific types of fuel tanks is essential for optimizing maintenance efforts and ensuring optimal performance. Let’s explore the best practices for automotive fuel tanks, industrial fuel storage tanks, aviation fuel tanks, and marine fuel tanks.
Automotive Fuel Tanks
Automotive fuel tanks are integral components of vehicles, storing fuel for combustion engines. To ensure the reliability and safety of automotive fuel tanks, the following best practices should be observed:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct visual inspections of automotive fuel tanks for signs of corrosion, leaks, or structural damage. Pay attention to vulnerable areas such as seams, welds, and mounting brackets.
- Fuel Quality Management: Use high-quality fuel from reputable sources to prevent contamination and fuel degradation. Monitor fuel quality parameters such as octane rating, ethanol content, and moisture levels.
- Preventive Maintenance: Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules for fuel tank components such as fuel filters, fuel lines, and fuel pumps. Replace worn or damaged parts promptly to prevent fuel system failures.
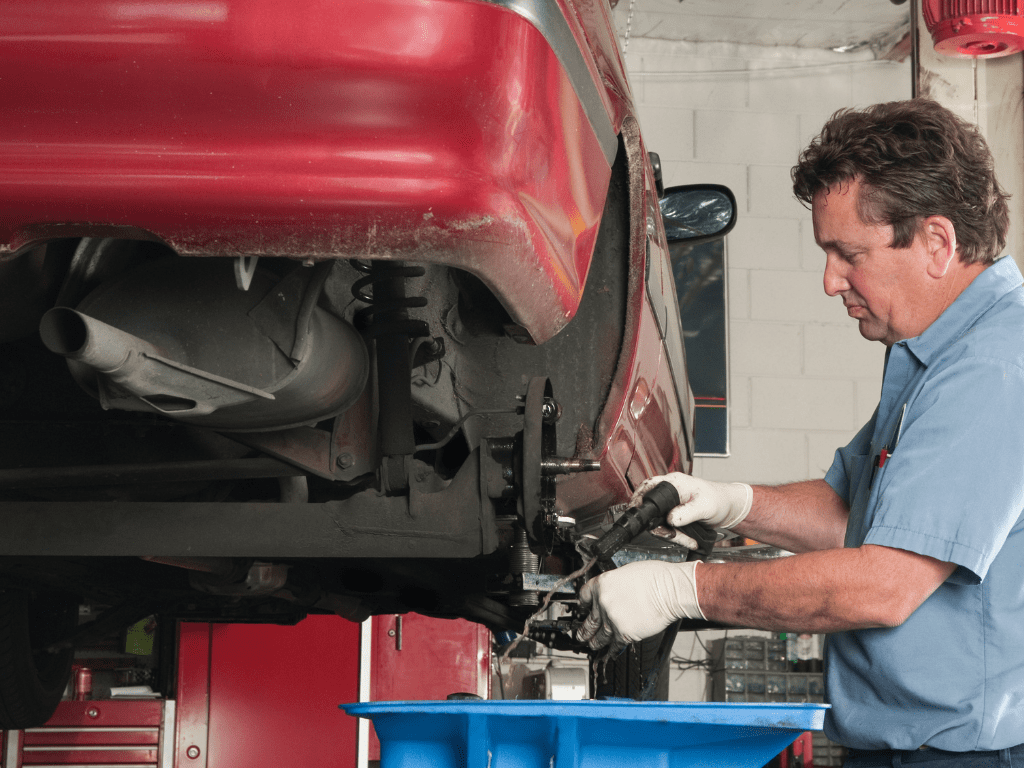
Industrial Fuel Storage Tanks
Industrial fuel storage tanks are used for bulk storage of fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene in various industrial facilities. Implementing proper maintenance practices is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of industrial fuel storage tanks:
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to regulatory requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of industrial fuel storage tanks. Ensure compliance with standards such as API 653 for aboveground storage tanks and API 650 for atmospheric storage tanks.
- Leak Detection and Monitoring: Install leak detection systems and monitoring equipment to detect leaks or spills in industrial fuel storage tanks promptly. Implement regular testing and inspection protocols to identify potential issues early on.
- Corrosion Prevention: Apply protective coatings and corrosion inhibitors to the interior and exterior surfaces of industrial fuel storage tanks. Implement cathodic protection systems to mitigate corrosion risks and extend the lifespan of the tanks.

Aviation Fuel Tanks
Aviation fuel tanks are critical for storing fuel onboard aircraft and ensuring safe and efficient flight operations. Maintaining the integrity and cleanliness of aviation fuel tanks is essential for aviation safety:
- Safety Protocols: Adhere to strict safety protocols for handling, storage, and maintenance of aviation fuel tanks. Follow industry best practices outlined by organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
- Precise Fuel Quality Control: Implement rigorous fuel quality control measures to ensure the purity and integrity of aviation fuel. Conduct regular fuel sampling and testing to monitor for contaminants and ensure compliance with aviation fuel specifications.
- Preventive Maintenance: Perform routine inspections and maintenance of aviation fuel tanks in accordance with manufacturer guidelines and regulatory requirements. Inspect fuel tank seals, fittings, and fuel lines for signs of wear or damage.

Marine Fuel Tanks
Marine fuel tanks are essential for storing fuel onboard ships, boats, and other marine vessels. Given the harsh marine environment, proper maintenance practices are crucial for preserving the integrity of marine fuel tanks:
- Managing Water Contamination: Implement measures to prevent water contamination in marine fuel tanks, such as using water-absorbing fuel filters and fuel additives. Regularly drain water from fuel tanks and monitor for signs of water accumulation.
- Special Considerations for Saltwater Environments: Protect marine fuel tanks from corrosion caused by exposure to saltwater by applying corrosion-resistant coatings and implementing corrosion prevention measures. Rinse and flush fuel tanks with freshwater regularly to remove salt deposits.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with maritime regulations and standards governing the design, construction, and maintenance of marine fuel tanks. Adhere to requirements set forth by classification societies such as Lloyd’s Register and the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS).

Advanced Technologies in Fuel Tank Maintenance
Advancements in technology have revolutionized fuel tank maintenance practices, offering innovative solutions for monitoring, cleaning, and protecting fuel storage systems. Leveraging these technologies can enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of fuel tank maintenance efforts:
Smart Monitoring Systems
Smart monitoring systems utilize sensors, telemetry, and data analytics to provide real-time insights into the condition of fuel tanks. These systems enable remote monitoring of key parameters such as fuel levels, temperature, pressure, and corrosion rates. By detecting abnormalities and trends early on, smart monitoring systems facilitate predictive maintenance, allowing operators to address issues proactively before they escalate.
Automated Cleaning Solutions
Automated cleaning solutions leverage robotics, high-pressure water jets, and chemical agents to remove contaminants and debris from fuel tanks efficiently. These automated systems eliminate the need for manual cleaning, reducing downtime and labor costs associated with traditional cleaning methods. Additionally, automated cleaning solutions ensure thorough cleaning of fuel tanks, improving fuel quality and system reliability.
Innovations in Corrosion Protection
Advancements in corrosion protection technologies offer effective solutions for mitigating corrosion risks in fuel tanks. Advanced coatings and linings provide superior protection against corrosion, extending the lifespan of fuel tank systems. Furthermore, new materials and formulations enhance the durability and performance of corrosion-resistant coatings, even in harsh environments. Cathodic protection systems continue to evolve, offering enhanced corrosion prevention capabilities and improved efficiency.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
Compliance with regulations and environmental considerations is paramount in fuel tank maintenance to ensure safety, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance:
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Fuel tank maintenance practices must align with relevant standards and regulations established by regulatory agencies and industry organizations. Organizations must adhere to guidelines such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards, and industry-specific codes of practice. Regular inspections, audits, and compliance assessments are essential to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
Environmental Impact
Minimizing the environmental impact of fuel tank maintenance activities is essential for sustainable operations. Preventing leaks, spills, and emissions through proactive maintenance practices helps protect ecosystems and natural resources. Organizations should implement spill prevention and response measures, as well as environmental management systems, to mitigate environmental risks associated with fuel tank maintenance. Additionally, investing in environmentally friendly technologies and practices, such as biodegradable cleaning agents and fuel additives, supports sustainable fuel tank maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fuel tank maintenance is not merely a routine task but a critical aspect of ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and safety of fuel storage systems across various industries. By addressing common issues such as contamination, corrosion, and structural integrity through regular inspection, cleaning, and preventive measures, organizations can minimize risks, optimize operational performance, and comply with regulatory requirements. Embracing advanced technologies such as smart monitoring systems, automated cleaning solutions, and innovative corrosion protection methods further enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of fuel tank maintenance efforts. Moreover, maintaining compliance with standards and regulations while minimizing environmental impact underscores the importance of responsible fuel tank maintenance practices for a sustainable future. With proactive maintenance and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can safeguard their fuel storage infrastructure, minimize downtime, and maximize the reliability of their operations for years to come.














