Introduction
A. Importance of Grease Traps in Commercial Settings
In commercial settings such as restaurants, hotels, and food processing facilities, the efficient management of grease and oil is essential for maintaining proper sanitation, preventing plumbing issues, and adhering to environmental regulations. Grease traps play a crucial role in this regard by intercepting fats, oils, and grease (FOG) from wastewater before it enters the sewage system. Failure to properly manage FOG can lead to costly plumbing problems, foul odors, and environmental pollution.
B. Understanding Grease Traps: Functionality and Maintenance
Understanding the functionality, maintenance, and solutions associated with grease traps is vital for ensuring the smooth operation of commercial kitchens and other facilities. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition and purpose of grease traps, the various types available, and essential maintenance practices to prolong their lifespan and efficiency. Additionally, we will explore innovative solutions, including specialized products like AquaQuick 2000, designed to enhance grease trap maintenance and performance.
II. What Is a Grease Trap?
A. Definition and Purpose
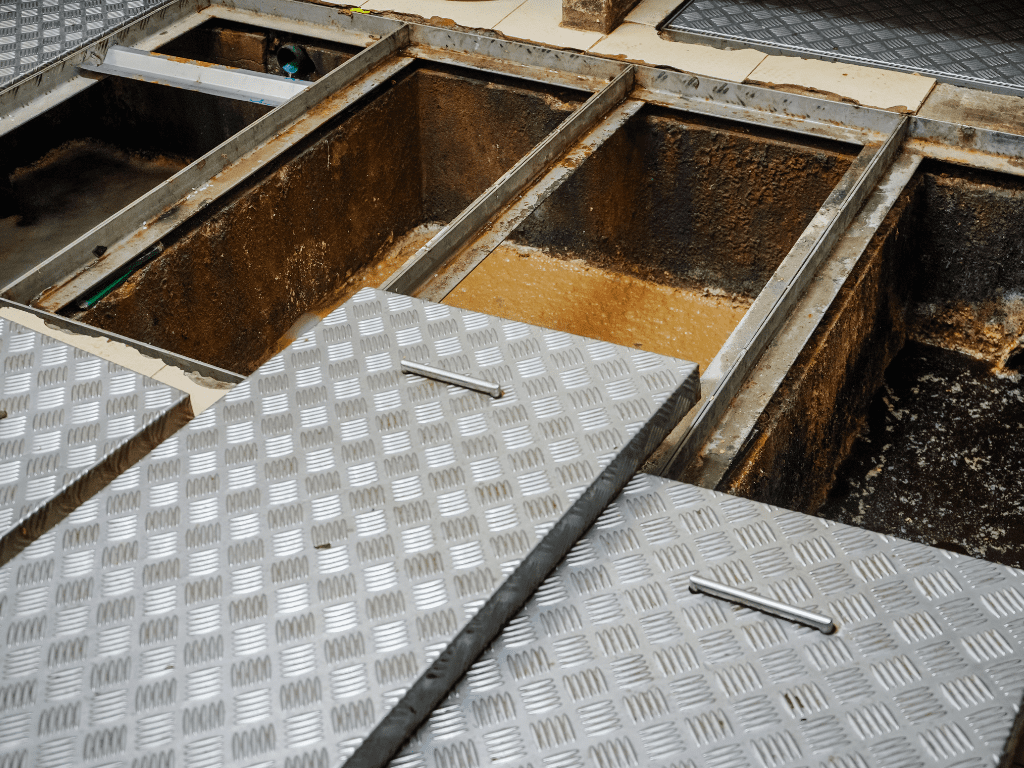
A grease trap, also known as a grease interceptor or grease separator, is a plumbing device designed to intercept and trap FOG, preventing it from entering the wastewater system. It consists of a tank-like container installed in the plumbing line, typically near the source of wastewater discharge, such as sinks, dishwashers, or floor drains. The primary purpose of a grease trap is to capture FOG, allowing the cleaner water to continue flowing into the sewage system.
B. Types of Grease Traps
1. Passive Grease Traps
Passive grease traps rely on the principle of gravity to separate FOG from wastewater. As wastewater flows into the trap, the velocity decreases, allowing FOG to rise to the surface due to its lower density. Meanwhile, solids settle at the bottom of the trap. The trapped grease forms a layer on top of the water, while the relatively cleaner water exits through an outlet pipe.
Passive grease traps come in various designs, including hydromechanical, gravity, and combination traps, each offering different levels of efficiency and maintenance requirements.
2. Automatic Grease Recovery Units (AGRUs)
Automatic grease recovery units (AGRUs) are advanced grease trap systems that employ mechanical devices to enhance the separation and removal of FOG from wastewater. Unlike passive traps, AGRUs are equipped with motors, pumps, and sensors to automate the grease removal process.
AGRUs utilize techniques such as skimming, centrifugation, or air flotation to efficiently extract grease from the wastewater stream. These units are ideal for high-volume commercial kitchens and facilities where manual grease removal may be impractical or insufficient.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore the operation, maintenance, and innovative solutions associated with grease traps, providing valuable insights for commercial operators seeking to optimize their grease management practices.

III. How Does a Grease Trap Work?
A. Mechanism of Operation
1. Gravity Separation
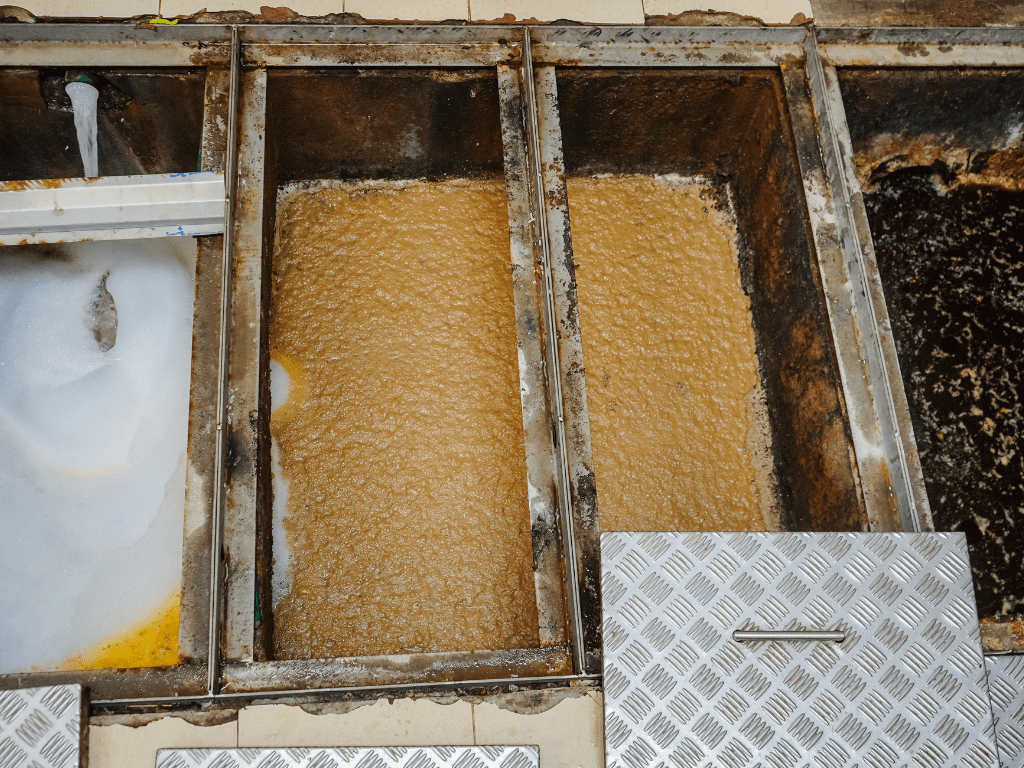
The primary mechanism behind the operation of a grease trap is gravity separation. As wastewater containing fats, oils, and grease (FOG) enters the trap, it undergoes a change in velocity. This decrease in velocity allows the heavier solid particles and denser liquids to settle at the bottom of the trap, while the lighter FOG floats to the top. This natural separation process occurs due to the differences in density between water and grease.
2. Retention Time
Retention time refers to the duration for which wastewater remains in the grease trap. Longer retention times allow for more effective separation of FOG from the water. The design and size of the grease trap determine the retention time, with larger traps typically providing longer retention times and better separation efficiency.
B. Key Components
1. Inlet
The inlet of a grease trap is the point at which wastewater enters the trap from the drainage system. It is designed to slow down the flow of water, allowing sufficient time for the separation process to occur. Inlet configurations may vary depending on the specific design of the grease trap.
2. Baffle System
The baffle system is a crucial component of a grease trap that helps to direct the flow of wastewater and facilitate the separation of FOG. Baffles are strategically placed within the trap to create turbulence and encourage the settling of solids while allowing FOG to rise to the surface.
3. Outlet
The outlet of the grease trap is where the relatively cleaner water exits the trap after the separation process. The outlet is typically located near the bottom of the trap to ensure that the trapped grease remains contained within the unit.
C. Working Process
1. Collection of Wastewater
Wastewater containing FOG enters the grease trap through the inlet. The trap slows down the flow of water, allowing it to undergo gravity separation.
2. Separation of Fats, Oils, and Grease (FOG)
As the wastewater moves through the trap, the FOG floats to the surface, forming a layer of grease. Meanwhile, solid particles settle at the bottom of the trap, forming sludge.
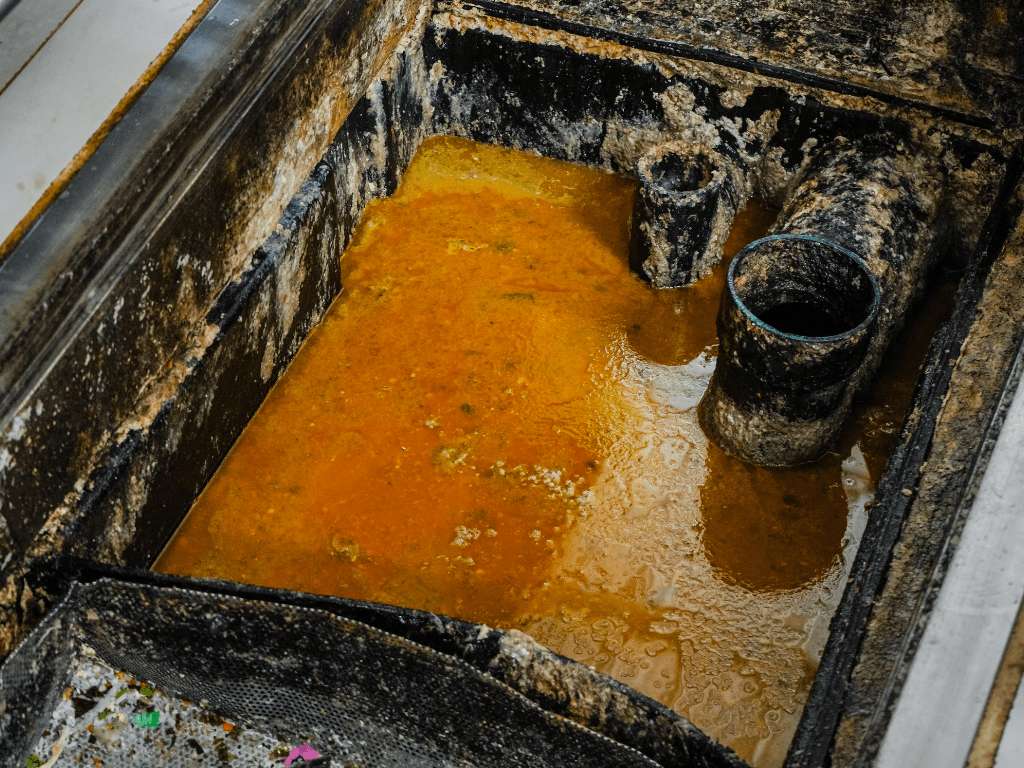

3. Effluent Discharge
Once the separation process is complete, the relatively cleaner water exits the grease trap through the outlet and continues into the sewage system. The trapped grease and solids remain within the trap until they are removed during routine maintenance.
IV. Importance of Grease Traps in Preventing Environmental Pollution
A. Role in Preventing Oil Spills
Grease traps play a crucial role in preventing oil spills by intercepting FOG from wastewater before it enters the sewage system. Without grease traps, FOG can accumulate in sewer lines, leading to blockages and potential spills that can contaminate waterways and harm aquatic life.
B. Environmental Impact of FOG Discharge
The discharge of FOG into the environment can have significant environmental impacts. When FOG enters water bodies, it can form thick layers on the surface, disrupting the natural balance of ecosystems and endangering marine life. Additionally, FOG can coat the feathers of birds, impairing their ability to fly and regulate body temperature.
C. Compliance with Regulations
Many jurisdictions have regulations in place that require commercial establishments to install and maintain grease traps to prevent FOG pollution. Compliance with these regulations is essential not only for environmental protection but also to avoid fines and penalties imposed by regulatory authorities. Grease traps help businesses meet these regulatory requirements by effectively managing FOG and preventing its discharge into the environment.
V. Maintenance and Cleaning of Grease Traps
A. Frequency of Maintenance
Regular maintenance of grease traps is essential to ensure their efficient operation and prevent issues such as clogging and foul odors. The frequency of maintenance depends on various factors, including the size of the grease trap, the volume of wastewater processed, and the types of food being prepared. Generally, grease traps should be inspected and cleaned at least every 1 to 3 months, although high-volume establishments may require more frequent maintenance.
B. Professional vs. DIY Cleaning
Business owners have the option to either perform grease trap maintenance themselves or hire professional services for this task. While some may opt for DIY cleaning to save costs, professional cleaning services often provide more thorough and efficient cleaning, ensuring that all grease and solids are properly removed from the trap. Additionally, professional cleaners are equipped with the necessary tools and expertise to safely handle grease trap maintenance.

C. Techniques for Cleaning Grease Traps
1. Pumping Out Accumulated Grease
One of the primary tasks in grease trap maintenance is pumping out accumulated grease and solids. This process involves using a vacuum truck to remove the contents of the grease trap and dispose of them properly. Pumping out should be done regularly to prevent the buildup of grease and solids, which can lead to blockages and reduced trap efficiency.
2. Scraping and Removing Solid Debris
In addition to pumping out grease, solid debris that accumulates at the bottom of the grease trap must be scraped and removed. This can be done using specialized tools such as scrapers and brushes to loosen and dislodge solid waste. Care should be taken to ensure that all debris is thoroughly removed to prevent clogs and foul odors.
3. Biological Additives for Grease Trap Maintenance
Biological additives, such as bacteria-based enzymes, can be used to aid in grease trap maintenance. These additives contain beneficial bacteria that break down organic matter, including FOG, into smaller, more manageable components. Regularly adding biological additives to the grease trap can help prevent the buildup of grease and reduce the frequency of manual cleaning.
D. Utilizing Specialized Solutions
1. Introduction to AquaQuick 2000
AquaQuick 2000 is a specialized solution designed to enhance grease trap maintenance and performance. It is a highly effective grease trap cleaner and degreaser that utilizes advanced surfactant technology to break down and emulsify grease, allowing for easier removal during cleaning.
2. Benefits of AquaQuick 2000 in Grease Trap Maintenance
- Superior grease-cutting properties: AquaQuick 2000 effectively breaks down even the toughest grease deposits, ensuring thorough cleaning of the grease trap.
- Non-toxic and environmentally friendly: AquaQuick 2000 is formulated using biodegradable ingredients, making it safe for use in commercial kitchens and environmentally sensitive areas.
- Reduces cleaning frequency: By preventing grease buildup, AquaQuick 2000 helps extend the time between manual cleanings, saving time and labor costs.
- Prevents foul odors: Regular use of AquaQuick 2000 helps eliminate foul odors associated with grease traps, creating a more pleasant environment for kitchen staff and customers.

3. Application Process and Effectiveness
AquaQuick 2000 can be easily applied to grease traps using a pump or sprayer. Once applied, it quickly penetrates and emulsifies grease, allowing it to be easily rinsed away with water. The effectiveness of AquaQuick 2000 in grease trap maintenance has been demonstrated in numerous commercial kitchens, where it has proven to be a reliable solution for keeping grease traps clean and odor-free.
E. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Foul odors: If foul odors persist despite regular cleaning, it may indicate that the grease trap is not being cleaned thoroughly enough. In such cases, it may be necessary to increase the frequency of cleaning or use specialized cleaning products like AquaQuick 2000.
- Slow drainage: Slow drainage may be caused by a buildup of grease or solids in the trap. Regular maintenance, including pumping out accumulated grease and removing solid debris, can help alleviate this issue.
- Blockages: If the grease trap becomes blocked, it may need to be manually unclogged using tools such as plumbing snakes or hydro-jetting equipment. Preventing blockages through regular maintenance is essential to ensure uninterrupted operation.
VI. Grease Trap Sizing and Installation Considerations
A. Determining Appropriate Size
The size of a grease trap should be determined based on factors such as the volume of wastewater generated, the types of food being prepared, and local regulations. Grease traps come in various sizes, ranging from small under-sink units to large external tanks, and selecting the appropriate size is essential to ensure effective grease interception.
B. Installation Guidelines
Grease traps should be installed by qualified professionals in accordance with local building codes and regulations. Proper installation ensures optimal performance and prevents issues such as leakage and improper drainage.
C. Location Considerations
Grease traps should be located as close to the source of wastewater discharge as possible to maximize efficiency. Additionally, they should be easily accessible for maintenance and cleaning purposes.

VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, grease traps play a critical role in commercial kitchens and food processing facilities by intercepting fats, oils, and grease from wastewater and preventing environmental pollution. Proper maintenance and cleaning are essential to ensure the efficient operation of grease traps, with options ranging from DIY cleaning to professional services and the use of specialized solutions like AquaQuick 2000. By adhering to best practices in grease trap maintenance and installation, businesses can ensure compliance with regulations, prevent costly plumbing issues, and promote a cleaner and safer environment for all.
FAQs:
Q: How often should I clean my grease trap?
A: The frequency of grease trap cleaning depends on several factors, including the size of the trap, the volume of wastewater generated, and the type of establishment. Generally, grease traps should be cleaned at least every 30 to 90 days. However, high-volume commercial kitchens may require more frequent cleaning, possibly every 30 days or even weekly. Regular inspections can help determine the optimal cleaning frequency based on the accumulation of grease and solids.
Q: What are some tips for maintaining a grease trap?
A: Proper maintenance is essential for the efficient operation of a grease trap. Here are some key tips:
- Schedule regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent grease buildup and ensure optimal performance.
- Train staff to minimize the amount of FOG entering the trap by scraping dishes and utensils before washing.
- Avoid disposing of grease, oil, and food scraps down the drain.
- Monitor the condition of the trap and perform visual inspections periodically to check for signs of damage or malfunction.
- Keep accurate records of cleaning schedules and maintenance activities for regulatory compliance.
Q: What are the best practices for installing a grease trap?
A: Proper installation is critical to the effectiveness of a grease trap. Here are some best practices:
- Consult local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance with installation requirements.
- Choose an appropriate location for the grease trap, considering factors such as accessibility, proximity to wastewater sources, and ventilation.
- Install the grease trap according to manufacturer guidelines and recommendations.
- Ensure proper sizing of the grease trap based on the anticipated flow rate and volume of wastewater.
- Use quality materials and components for installation to prevent leaks and ensure durability.
Q: What are the benefits of using a grease trap?
A: Grease traps offer several benefits for commercial establishments and the environment:
- Prevents grease buildup in sewer lines, reducing the risk of blockages and costly repairs.
- Protects the integrity of the sewage system by minimizing the discharge of FOG into the environment.
- Helps maintain proper sanitation and hygiene in commercial kitchens by preventing foul odors and backups.
- Enhances regulatory compliance by meeting requirements for grease management and pollution prevention.
- Supports sustainability efforts by promoting responsible wastewater management and reducing environmental impact.